Introduction
Gas is one of the fundamental states of matter, alongside solids and liquids. However, unlike solids and liquids, gases do not have a fixed shape or volume. Therefore, to understand gases better, it is helpful to group them based on their behavior, origin, and uses. As a result, the sections below provide a detailed breakdown of the main types of gas.

Type of gases
1. Natural Gases
Natural gases are found in nature without being created by human processes. Many of them are essential for life on Earth.

Oxygen
Oxygen is vital for respiration in humans, animals, and many other living organisms. In addition, it supports combustion, which means fires cannot burn without it.
Nitrogen
Nitrogen makes up the largest portion of Earth’s atmosphere. However, although most living beings cannot use nitrogen directly, it is still crucial for plant growth and soil fertility.
Carbon Dioxide
Carbon dioxide is released during breathing, the burning of fuels, and natural processes such as volcanic eruptions. Meanwhile, plants use it during photosynthesis to produce food.
Water Vapor
This is the gaseous form of water. It plays a major role in weather patterns, humidity, and the water cycle.
2. Noble (Inert) Gases

Noble gases are known for their low chemical reactivity. They rarely combine with other elements, which makes them stable and safe for many applications.
Helium
Helium is lighter than air and commonly used in balloons and airships. It is also used in medical and scientific equipment.
Neon
Neon produces a bright glow when electricity passes through it, which is why it is widely used in advertising signs.
Argon
Argon is often used in welding to protect metals from reacting with oxygen during high-temperature processes.
Other noble gases include krypton, xenon, and radon, each with specialized uses.
3. Industrial Gases
Industrial gases are manufactured for commercial and technical purposes. They are widely used in factories, laboratories, and hospitals.

Hydrogen
Hydrogen is a clean-burning fuel and is gaining attention as an alternative energy source. It also serves in chemical manufacturing.
Acetylene
Acetylene produces a very hot flame and commonly serves for welding and metal cutting.
Industrial Oxygen and Nitrogen
These gases find use in steel production, food packaging, electronics, and healthcare.
4. Greenhouse Gases
Greenhouse gases trap heat in Earth’s atmosphere. This natural process keeps the planet warm, but excess amounts contribute to climate change.
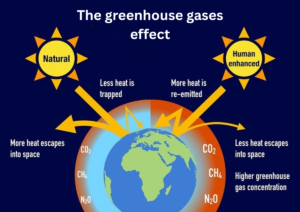
Carbon Dioxide
Produced by burning fossil fuels and deforestation, it is the most discussed greenhouse gas.
Methane
Methane releases from natural sources like wetlands and human activities such as agriculture and waste management. It traps more heat than carbon dioxide over short periods.
Nitrous Oxide
This gas comes from agricultural activities and industrial processes and contributes to global warming.
5. Toxic and Poisonous Gases
Some gases are extremely harmful to humans, animals, and the environment, even in small amounts.Toxic gas and Poisonous gas are among from them.

Carbon Monoxide
Incomplete combustion produces this colorless and odorless gas. It is very dangerous because it reduces oxygen delivery in the body.
Chlorine
Used for disinfecting water, chlorine gas can be toxic when inhaled in high concentrations.
Sulfur Dioxide
Released from burning coal and volcanic eruptions, sulfur dioxide can irritate the respiratory system and contribute to acid rain.
6. Fuel Gases
Fuel gases burn to produce energy for cooking, heating, and power generation.
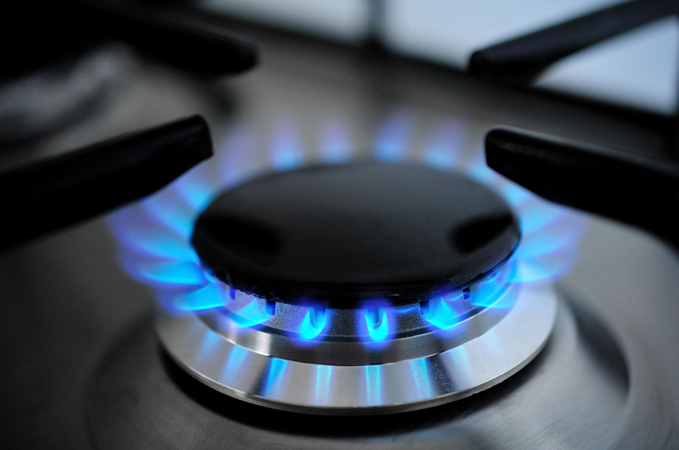

Natural Gas
Commonly used in homes and power plants, natural gas burns cleaner than coal and oil.
Liquefied Petroleum Gas (LPG)
LPG users widely employ it for cooking and heating, especially in areas without pipeline gas.
Biogas
Produced from organic waste, biogas is a renewable energy source and helps reduce waste pollution.
7. Medical Gases
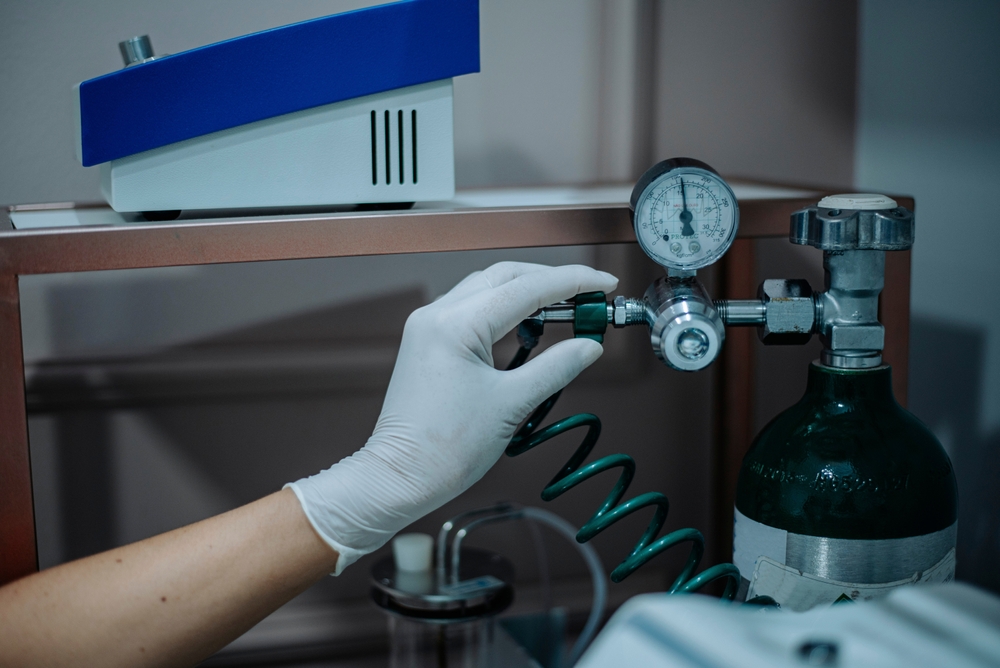

Medical Oxygen
Used to support patients with breathing difficulties and, furthermore, during surgeries.
Nitrous Oxide
Often called laughing gas, doctors use it as a mild anesthetic and pain reliever.
Medical Air
A clean, controlled mixture of gases used in ventilators and other medical equipment.
Conclusion
While gases are often unseen, they nevertheless exert a significant influence. In fact, they support life, power industries, and shape everyday processes. Moreover, gases play a crucial role in influencing climate systems and advancing healthcare. As a result, different types of gas affect our world in countless ways. Therefore, understanding these categories helps us use gases safely, efficiently, and responsibly.