Introduction
Programming languages act as the intermediary between human ideas and computer operations,allowing programmers to develop software applications and systems that drive the digital realm.In this comprehensive manual,we will explore the definition of programming languages,their importance in computer systems and the different types of programming languages utilized in contemporary computing.
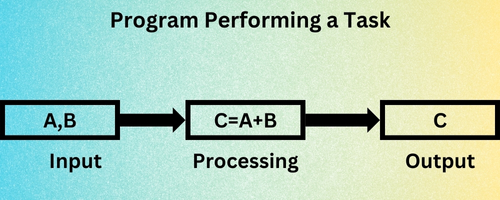
- The computer has become an indispensable tool in the modern era. It possesses the remarkable capability to handle a vast range of operations, encompassing the reception of data, its subsequent processing, and the generation of meaningful outputs. Despite these impressive abilities, the computer is, at its core, a machine, and therefore incapable of independent action. Even the most elementary operation, such as the addition of two numbers, necessitates explicit instructions. To function effectively, computers rely on a structured sequence of instructions, commonly known as a computer program, that precisely delineates the procedures for task execution.
- Consider this: it's much like a manager or team lead communicating directives to their team. The team then executes these instructions, and their work is organized accordingly. In a comparable way, a computer also operates based on received guidance; it ingests instructions, provided as computer programs, and then completes the given job.
- A program, fundamentally, comprises a sequence of commands, dictating a computer's actions to achieve a defined goal. These instructions are authored in a human-readable, high-level programming language, compatible across diverse processing units. Think of it this way: programs and recipe books share similarities. Each recipe, much like a program, outlines a specific procedure.Consider each recipe as a distinct program. It features two key components: the ingredients, representing fixed or input data, and a set of step-by-step instructions specifying how to manipulate those ingredients. The act of preparing a dish from a recipe is, in essence, the execution of that program.
Now the question arises that how human beings instruct computers. We, as human beings, use natural languages such as English,Spanish or French to communicate.Similarly an user communicates with the computer in a language understood by it. Note that human beings cannot interact directly with the computer using natural languages because, thus far,we have not developed such computers that can comprehend natural languages. Rather, the instructions, provided in the form of computer programs,are developed using computer or programming languages.
Developing of a computer program
- The instructions to be performed.
- The order in which those instructions are to be performed.
- The data required to perform those instruction.
Key aspects of programming languages
- Syntax refers to the organization and regulations governing the writing of code, encompassing elements such as keywords, symbols, and grammar.
- Semantics refer to understanding and interpreting code statements, which dictates the logic and operations of programs.
- The journey from human-friendly code to the machine's language, that is the implementation. This involves the conversion of code, designed for human readability, into a sequence of instructions the machine can execute. To do this, we use tools like compilers and interpreters.
Types of Programming Languages
Programming languages are divided into groups according to their functionality, design, and degree of abstraction. The primary programming language families found in contemporary computer systems are as follows:
High-Level Programming Languages
High-level languages abstract away complicated machine-level details in order to make them easily readable and understandable by humans. They provide libraries, data structures, and built-in functions that make coding easier. High-level programming languages include, for instance,
- Python: Python, a programming language known for its ease of use and adaptability, finds extensive application across various fields. It's a common choice for building websites, for the creation of software designed for data examination, and is also prevalent in artificial intelligence research, as well as scientific calculations.
- Java: Java's popularity stems from its suitability for building dependable enterprise applications, mobile software on Android, and large-scale systems. A key feature is its cross-platform capability, achieved through its interaction with the Java Virtual Machine (JVM).
- C#: Crafted by Microsoft, C# is a programming language employed in the .NET framework. Its application spans a range of software endeavors, including the development of desktop programs, web-based applications, and video games.
- JavaScript: Presently, JavaScript stands as a versatile programming language. Its application spans beyond the web application's user interface; it's also employed for backend development, with Node.js facilitating server-side scripting.
Low-Level Programming Languages
- Assembly Language: These mnemonic codes represent elements within a hierarchical system. They find application in core system programming and the development of internal driver software.
- C/C++: C is a procedure language that is designed for its efficiency and portability. On the other hand, add object-oriented C++ with wide applications in system software, games and critical performance applications.
Scripting Languages
Languages designed for programming serve several purposes, including quickly building prototypes, automating repetitive tasks, and creating scripts for applications. Often, they are interpreted rather than compiled, offering adaptability and enabling faster development processes.Scripting languages examples include:
- Bash: The shell programming language used for unix/linux systems that used for automation of system administration tasks and writing command line scripts.
- Perl: Very well known for its text processing capabilities, Perl targets system administration, web development, and network programming areas.
- Ruby: With a wide range of functionalities, Ruby is a practical language that is effectively utilized for web development (Ruby on Rails framework), scripting, and automation.
Functional Programming Languages
Functional programming languages focus on functional programming paradigms, which prioritize immutable data structures and treat functions as first-class citizens. A few instances are:
- Haskell: Celebrated for its rigorous static typing and purity, Haskell is utilised by academics, financial applications as well as people who teach functional programming.
- Erlang: Crafted for concurrent, parallel programming, Erlang’s uses include telecommunication systems, messaging platforms, and real-time software.
Domain-Specific Languages (DSL)
Domain-specific languages provide specialized features and abstractions and are designed for particular domains, industries, or problem domains. As examples, consider:
- SQL (Structured Query Language): A language that is used for the management of database and querying, this can be applied in database systems and data analytics.
- HTML/CSS: Instruction languages like Markup and Styling for creating web pages and user interfaces.
- R: A language for statistics with a computing and data analysis focus implemented in the field of data science and machine learning.
How crucial is programming languages for today’s computer systems?
- Versatility: Programming languages are not general-purpose. Different ones suit a particular task and field more than the others, giving developers the abilities to pick their preferred tools for the project.
- Efficiency: Language choice can, however, affect system performance, resources management and overall development efficiency.
- Compatibility: Programming languages are enabling conversable interface among different software components, systems, and platforms, so that system integration becomes smoother.
- Innovation: It is the new programming languages and programming paradigms that introduce innovation to the field of software development which in turn enables to solve rapidly evolving problems and seize new opportunities.
- Community and Ecosystem: Most of programming languages have open source communities, libraries, frameworks and tools whose purpose is to likes developers and help to collaboration.