Introduction
Fuel is essential in chemical engineering, powering machinery and enabling reactions critical for efficiency and sustainability. This blog explores various fuels used in the field, detailing their characteristics, applications, and environmental impacts.
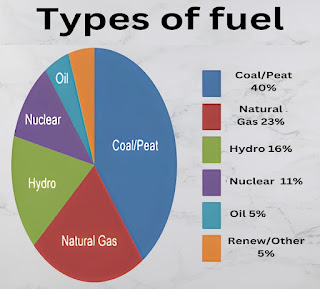
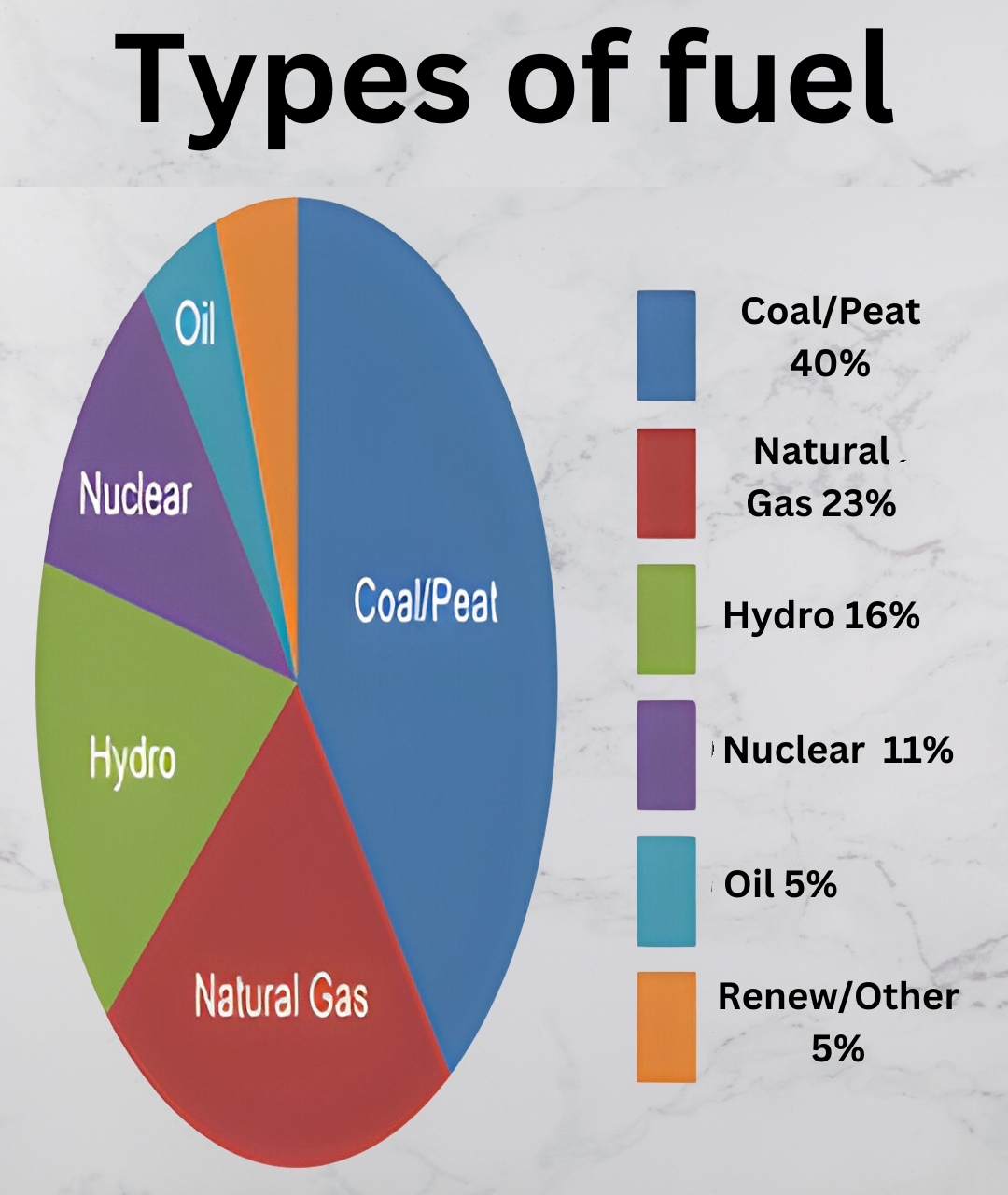
1.Fossil Fuels
- In chemical engineering, gasoline, diesel, and jet fuel serve as key energy carriers for their high energy content and accessibility.
- Natural gas is favored for its lower carbon footprint compared to other fossil fuels, making it a more appealing choice.
2.Renewable Fuels
3.Nuclear Fuels
4.Electricity
- Used in some chemical processes, direct electric heating replaces traditional fuels by feeding electricity directly into heating, reducing associated emissions.
5.Hybrid Systems
6.Synthetic Fuels
- Synthetic Natural Gas (SNG), produced by gasifying biomass or carbon-based feedstocks, serves as an alternative natural gas system.
- Technologies that clean carbon dioxide and convert it into synthetic fuels offer a promising solution for reducing emissions and addressing global climate change.
Conclusion
In chemical engineering, choosing the right fuel is key to balancing energy needs and environmental concerns. Engineers can select from fossil fuels to synthetic and renewable options, considering both economic and ecological factors. As the field evolves, creating cleaner, more efficient fuels remains central to sustainable progress.