Introduction
Electronic gadgets are now essential to practically every aspect of modern existence, from straightforward smartphones to intricate industrial equipment. The building blocks of these gadgets critically hinge on the substances from which they're made. From a vast assortment of materials come the different electronic parts, each material providing specific characteristics and serving its own particular purpose within the device.This blog post will delve into the diverse materials frequently employed in the electronics industry, exploring their specific functions and broad range of applications.
Understand the material used in electronics
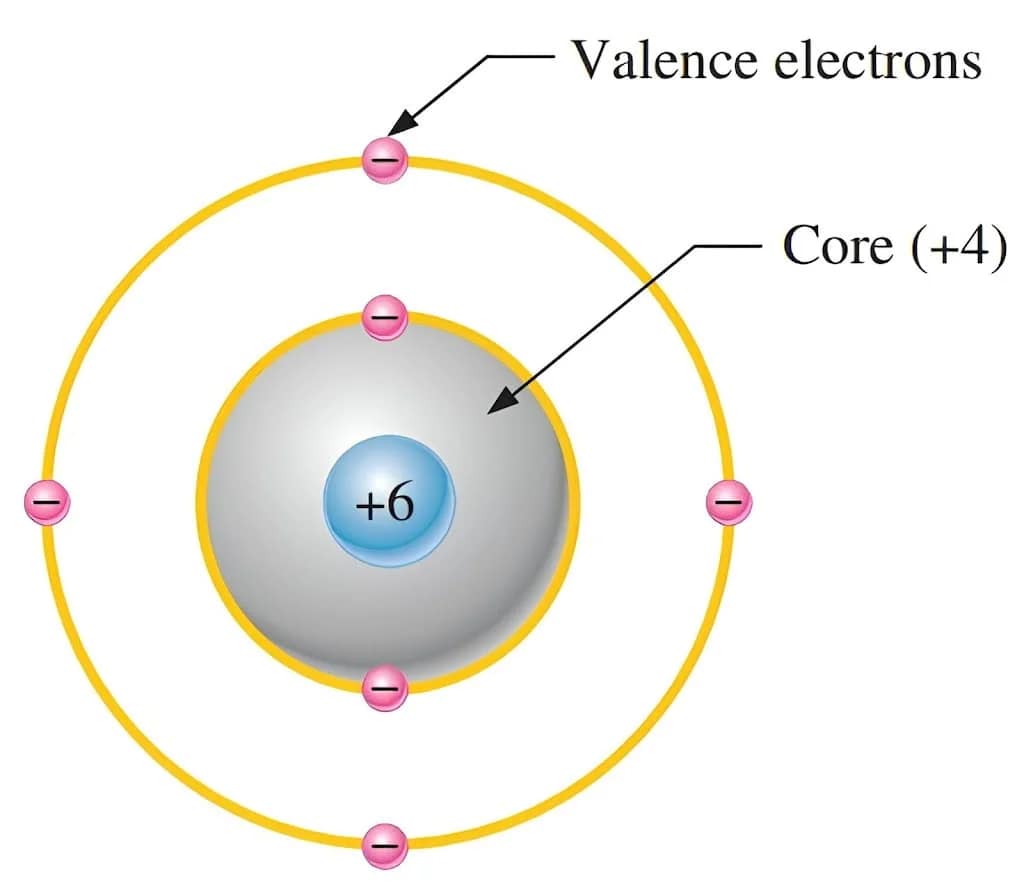
- Every substance is constructed from atoms. These fundamental units dictate a material's electrical behavior, especially its capacity to facilitate the flow of electrical charge.When examining electrical attributes, an atom can be conceptually simplified as comprising a valence shell, combined with a core encompassing all internal shells alongside the atom's central nucleus.
- This concept is illustrated in Figure 1 for a carbon atom. Carbon is used in some types of electrical resistors. Notice that the carbon atom has four electrons in the valence shell and two electrons in the inner shell. The nucleus consists of six protons and six neutrons, so the +6 indicates the positive charge of the six protons.
- The core has a net charge of +4 (+6 for the nucleus and -2 for the two inner-shell electrons).
Figure 1
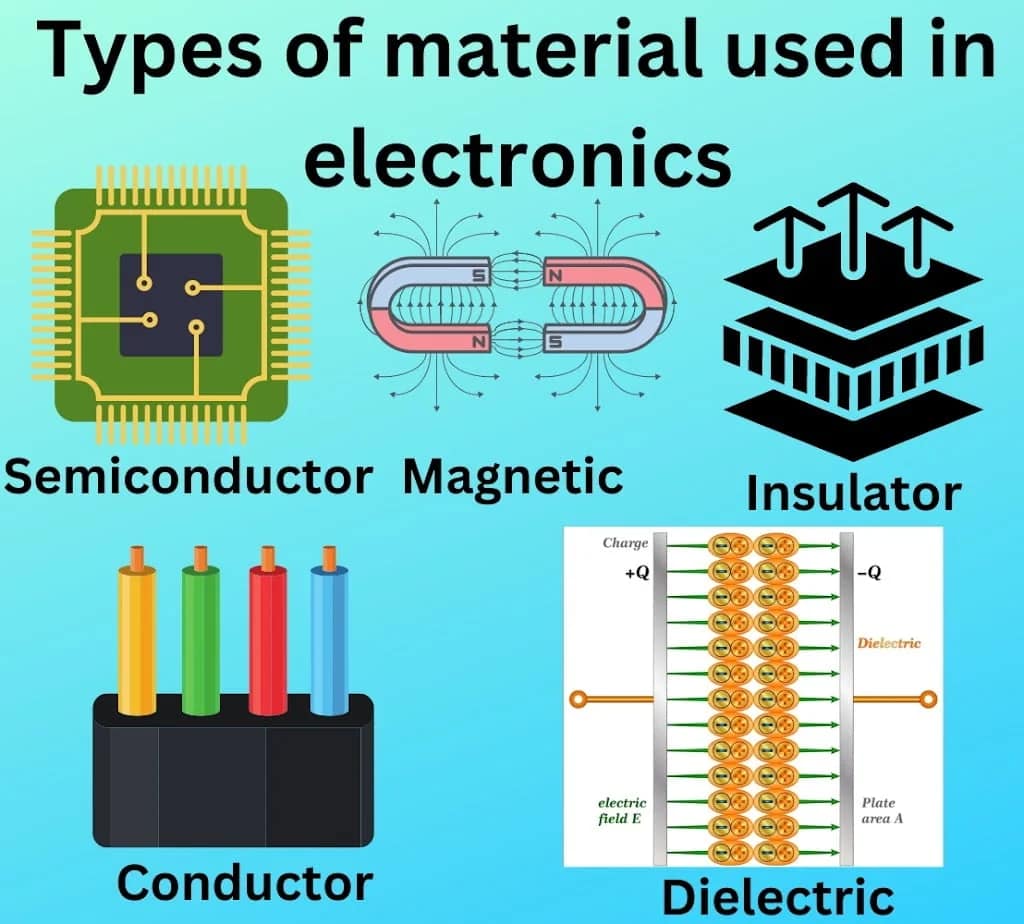
Types of material used in electronics
Conductors
Conductors are materials that give passage to the electrical current with minimum or little disruption. These are nothing without the help of which. They enable components in electronic circuits to be wired together.Common conductor materials include
- Copper: The appeal of copper lies in its outstanding electrical conductivity, coupled with its affordability. These characteristics have made it a popular choice in the realm of electrical wiring and within the traces found on printed circuit boards (PCBs).
- Aluminum: Despite copper's superior conductivity, aluminum offers advantages. It's significantly less heavy and more affordable. These qualities make it suitable for applications like electrical power lines and the fins in radiators, where weight and cost-effectiveness are important considerations.
Semiconductors
The semiconductor is the material, which lies between a conductor and an insulator with respect to its conductivity. They are very important in electronic machinery, as they are mainly in the driving circuitry of transistors and diodes.Key semiconductor materials include
- Silicon: Silicon reigns supreme as the go-to material in the realm of semiconductors. This is largely due to its exceptional stability and widespread availability, which makes it ideal for the manufacture of Integrated Circuits (ICs) and the diminutive yet powerful Microchips.
- Gallium Arsenide (GaAs): Implemented in the high frequency application such as microwave circuits and optical devices because of higher electron mobility of silicone compare to silicon.
Insulators
The insulators are, thus, materials that prevent the flow of electric current. They are, therefore, a very vital part for the isolation of the conductive elements and they prevent short-circuiting too.Common insulating materials include
- Glass: Used in electronics, for example, touch screens, because of its electrical insulation and transparency.
- Ceramic: Possessing remarkable thermal stability, ceramics also demonstrate a substantial capacity to withstand high dielectric fields. Consequently, these materials find application in capacitors, as insulating platforms, and within the construction of printed circuit boards.
Magnetic Materials
Magnetically susceptible materials exhibit magnetic properties, finding broad application within electronic components such as transformers, inductors, and magnetic storage devices.Examples include
- Iron: Expensive metallic because it has a high value of magnetic permeability and saturation flux density.
- Ferrites: Here are ceramic subsstances with high resistivity and high magnetic permeability, a good choice for inductor cores and EMI suppression.
Dielectric Materials
Dielectric or insulating materials are those with high electrical polarizability that are, hence, suitable for capacitors as well as energy storage devices.Common dielectric materials include.
- Polypropylene: Polypropylene capacitors, distinguished by their minimal dielectric loss and elevated breakdown voltage, find their application in both audio devices and power electronics.
- Tantalum Pentoxide (Ta2O5): Used in tantalum capacitors for their high capacitance per volume and stable electrical properties.
Applications of material used in electronics
- Within diverse electronic devices, from the simplest to the most complex, copper and aluminum pathways serve as essential conductors for electrical currents.The fundamental building block of integrated circuits, those ubiquitous components present in computers, mobile phones, and domestic appliances, relies heavily on silicon semiconductors.
- Non-conductive substances, including glass and ceramics, find applications in displays, circuit boards, and protective housings.Materials exhibiting magnetic properties, like iron and ferrites, are crucial components in transformers, inductors, and magnetic data storage devices.
- Dielectric materials like polypropylene and tantalum pentoxide enable the efficient operation of capacitors for energy storage and signal filtering.
Conclusion
The multiplicity of substances used in electronics demonstrates the richness, and the intricacy of modern electronics and technology. The conductors and semiconductors, insulators and magnetic materials function as a whole in order to provide essential functionality, performance and reliability of electronic systems spread across many sectors. Analyzing these materials and their uses is vital for the whole technical team and newbies as well in the area of electronics.